Things That Diabetes Patients Should Know About Liver Disease
As the diabetes causes due to damage of pancreas, there is a connection between diabetes and the pancreas. But you may wonder how the liver fits into this equation? Here is the answer to your question.
Diabetes increases the risk of kidney disease, nerve damage, blood vessel damage, infections, blindness and heart disease, but you may not realize diabetes can have profound effects on the liver as well.
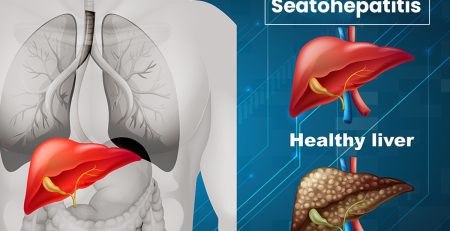
It has been observed that, Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects up to one-third of the entire adult population in industrialized countries. Person with type-2 diabetes is at more risk of having NAFLD. NAFLD is a broad term that includes several subtypes of liver diseases and clinically distinct conditions, like fatty liver and more serious steatohepatitis (NASH), with or without fibrosis (scarring), that can progress to liver cirrhosis and, in a few cases, to liver cancer. A liver biopsy may be recommended by liver specialists when blood tests for liver function are repeatedly and chronically elevated (e.g., for 6 months) and all other evaluations for the cause of the elevations are inconclusive.
Dr. Harshal Ghadikar 16th April FM Intervies
So What Is All The Fuss About?
With the increasing heart disease in those with diabetes patients, the liver problems are also increasing. And it is almost twice as high as having cardiovascular disease! Patients with diabetes have an increased incidence of severe fibrosis (thickening and scarring of connective tissue). Study also shows that, cirrhosis accounted for 12.5 percent of deaths in patients with diabetes. Cryptogenic cirrhosis in those with diabetes is also caused by NAFLD and is now the 3rd leading reason for liver transplantation.
A patient’s prognosis worsens with each stage of liver disease. But, not everyone’s liver disease progresses. Liver biopsy is used to determine the liver disease progression.
What Is Known About Possible Treatments?
Many studies say that the weight loss decreases liver fat and hence most recommended treatment. Low-glycemic, low-calorie diets with a weight loss of 2.2 – 4.4 pounds (1 to 2 kilograms) per week has been recommended. Low-fat diets should be avoided. Some experts suggest a Mediterranean diet (defined as high in complex carbohydrates or starches, high in monounsaturated fats – i.e., oils, moderate amounts of wine, and low amounts of red meat) is preferred in individuals with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD. Also alcohol consumption should be strongly avoided not only because of its toxic effects on the liver, but also because of its high calorie content. Daily exercise improves insulin action for everyone. Some medications are also used for the treatment of diabetes can also be beneficial for the liver.
Take-Home Message:
You’re now armed with the knowledge necessary to help take care of your liver and prevent diabetes related complications from affecting this vital organ. So, take a steps towards healthy life and lose weight, improve your diet, limit or avoid alcohol consumption and follow your doctor’s recommendations for controlling other conditions as well.
If you are diabetes patient and worried about risk of liver disease contact immediately to Gadhikar Clinic. Dr. Harshal Gadhikar is experienced liver specialist, gastroenterologist at Gadhikar Clinic. He has treated many patients with complex liver diseases.






Leave a Reply